Application Note
MaxCyte® Enables Development of New, Rapid, Sensitive SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Test
Background
The COVID-19 pandemic has killed millions worldwide since it emerged in December 2019, causing widespread social and economic strain. Testing is a crucial component in the public health response, and continued research to understand the disease and implement effective interventions against it is essential.
Currently, the most widely used method to diagnose active COVID-19 infections is by detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA with real-time reverse transcription PCR amplification. Another diagnostic approach is antibody testing. Infection with SARS-CoV-2 is determined by detecting the antibodies that the body produces in response to the virus. It takes about two weeks to build up a detectable level of antibodies in the bloodstream. While Some antibodies (IgA and IgM) are produced rapidly in response to infection and are quickly cleared; others (IgG) take longer to be found at detectable levels in circulation. Determining the presence of different isotypes can help differentiate between active and past infections.
There are several antibody tests, each with benefits and drawbacks. Lateral flow immunoassays take less than 20 minutes, but they are insensitive and the results are purely qualitative. Quantitative tests such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and chemiluminescent immunoassays are much more sensitive, but they can take hours and have challenging protocols with manual washing or complex fluidics steps. MaxCyte Flow Electroporation® technology is helping researchers develop and implement a new diagnostic test that overcomes these limitations and is quick, sensitive and easily adaptable as novel pathogenic strains emerge.
In this new approach, researchers use a technology called biolayer interferometry (BLI). This optical technique measures the interference pattern of white light reflected off two separate surfaces: an internal reference layer and a biosensor coated with immobilized proteins (antigens). When an antibody binds to proteins on the biosensor, it causes an increase in optical density. This results in a shift in the reflected lights’ wavelength which can be detected in real-time.
This real-time analysis can be used to gain insight into binding specificity, avidity and antibody concentration with accuracy and precision. Here, researchers investigated whether this technology could be used to detect the presence of antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD).
A key factor affecting the efficacy of this diagnostic approach is the large-scale production of high-grade RBD proteins that are used as antigens on the biosensor. MaxCyte® was able to reliably produce high-quality antigens which enabled the rapid and sensitive detection of SAR-CoV-2 antibodies from clinical samples.
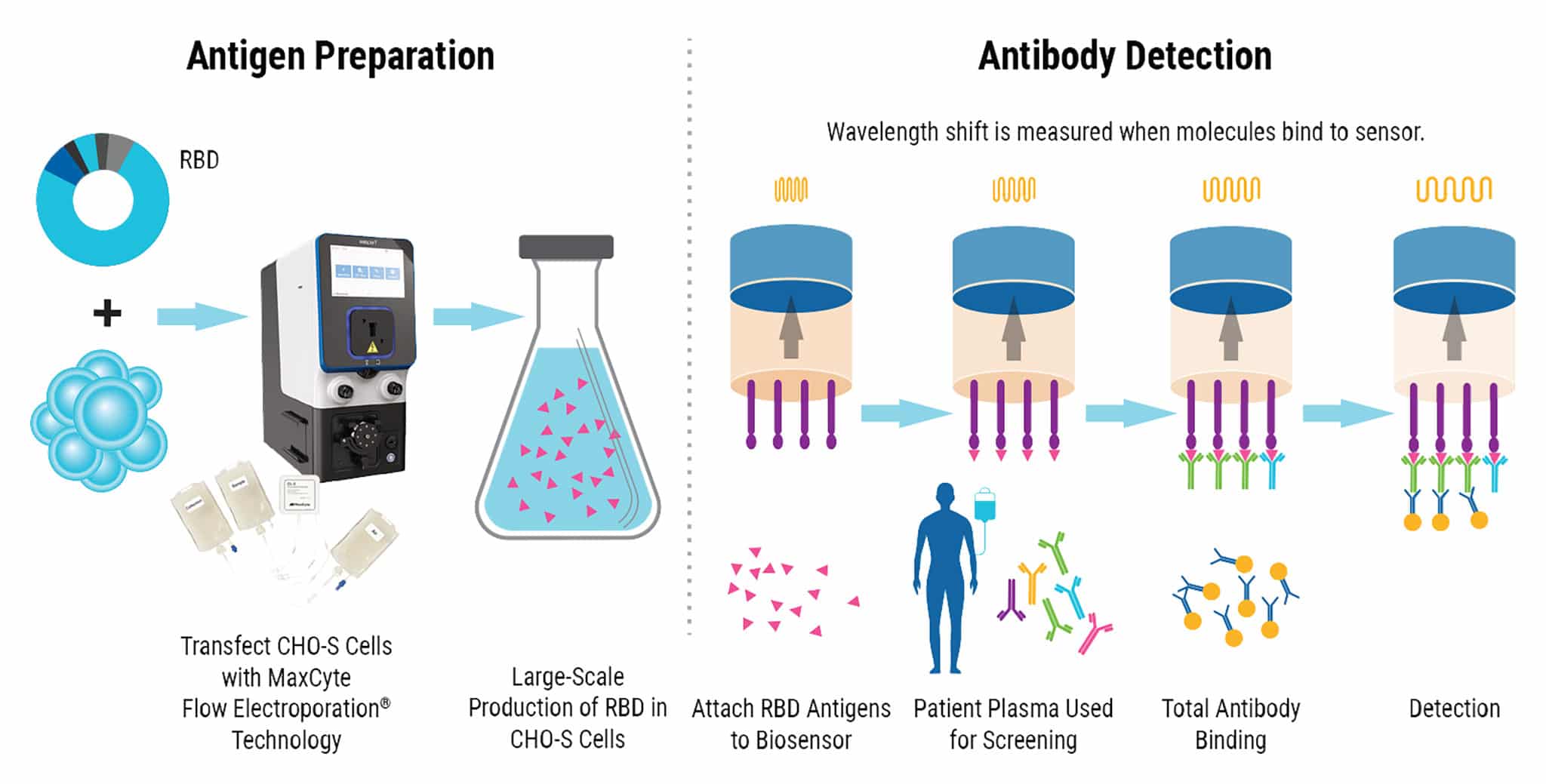
Experimental Design
CHO-S cells are transfected with an expression plasmid for RBD using MaxCyte® electroporation. Antigen is then harvested and purified from the cells. Biosensors are dipped into RDB antigens and then used to test plasma for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. As antibodies bind to the RBD antigens, real-time measurements record the change in the reflected wavelength of light over time, resulting in semi-quantitative detection of the antibodies present in patient plasma.
Aim
The aim of the study was to develop a biolayer interferometry immunosorbent assay (BLI-ISA) for SARS-CoV-2 antibody detection. MaxCyte Flow Electroporation® technology was critical in extending the application of BLI-ISA to SARS-CoV-2 screening by reliably producing RDB antigens for the biosensor. The new diagnostic assay uses a simple automated process that takes fewer than 20 minutes and delivers real-time measurements of total and isotype-specific antibody levels.
Method Overview
Below is a summary of RBD antigen production and the major steps involved in the BLI-ISA protocol. The procedure below demonstrates how MaxCyte Flow Electroporation® technology seamlessly fits into the streamlined workflow for SARS-CoV-2 screening.
- Plasmid Generation The expression plasmid for RBD was made by sub-cloning cDNA encoding the protein into a derivative of pcDNA3.1.
- Antigen Production CHO-S cells were transfected with the RBD expression plasmid using MaxCyte electroporation. Cells were incubated for 8 days at 32 °C, then centrifuged.
- Protein Purification Proteins were eluted through a StrepTrap® column. The fractions were dialyzed, biotinylated, and further purified by size exclusion chromatography before flash freezing at -80 °C for future use.
- Biosensor Preparation BLI-ISA was carried out on an Octet® RED384 instrument using tilted bottom 384-well plates. Anti-biotin biosensors were pre-equilibrated in buffer for 10 minutes before beginning the assay.
- Antigen Loading After equilibration, the biosensors were dipped into a solution of RBD antigen.
- Total Antibody Binding The antigen-loaded sensors were washed and dipped into a diluted patient serum sample. Real-time measurements are recorded as the change in reflected wavelength over time. Wavelength shift was recorded after 10 minutes.
- Detection The sensors were washed again and then dipped into a secondary antibody solution (colloidal gold-conjugated anti-human IgG). Wavelength shift was recorded after 3 minutes.
Results
Total and Specific Antibody Detection
To validate the BLI-ISA method, 10 plasma samples from recovered COVID-19 patients (presumed positive for antibodies) and 27 plasma and blood serum samples taken in 2016 and 2017 (before the COVID-19 pandemic) were tested. All samples were evaluated at 1:8 dilution with antigen-coated sensors and with no-antigen sensors.
Eight out of 10 positive samples were definitively identified by Total Antibody Binding (Figure 1). In the Detection step, all ten positive samples showed signal above background. The trends were consistent with previous ELISA analysis of the same samples.
Figure 1

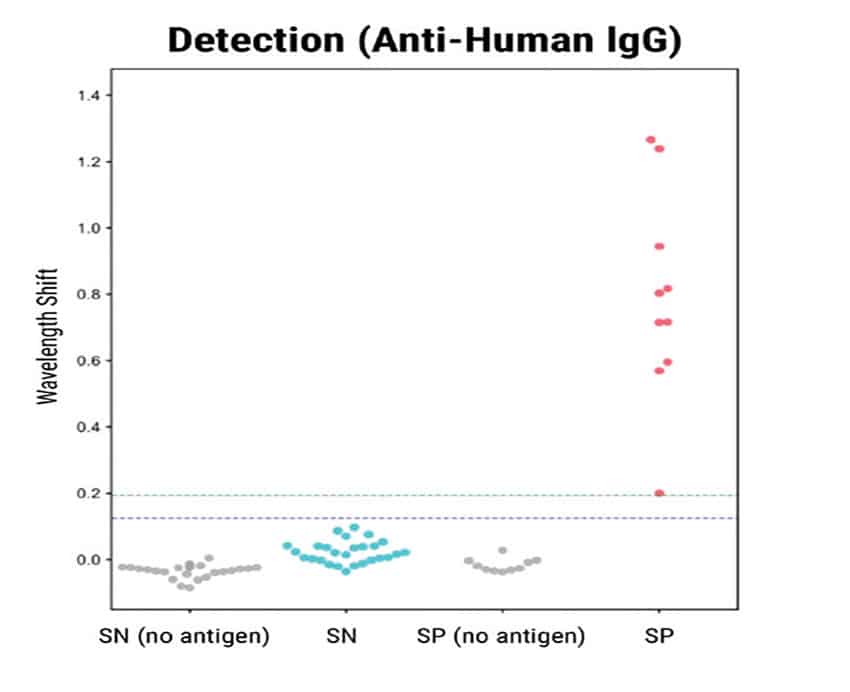
Figure 1. BLI-ISA evaluation of RBD-reactive human antibodies in human samples. BLI-ISA assay was used to measure SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies from patient plasma. SN is seronegative, SP is seropositive. Assays were performed at 1:8 dilution. Dots represent the mean of biological duplicates for a given sample. Blue and green dashed lines represent the mean of all seronegative samples plus 3 and 5 standard deviations.
Specific SARS-CoV-2 Detection
To assess the specificity of the BLI-ISA method, the researchers tested antigen binding with commercially obtained rabbit antibodies towards the Spike proteins of either SARS-CoV-2 or HCoV-HKU1 (another coronavirus known to infect humans). The positive control was a human SARS-CoV-1 antibody known to have cross-reactivity with the SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD.
Figure 2
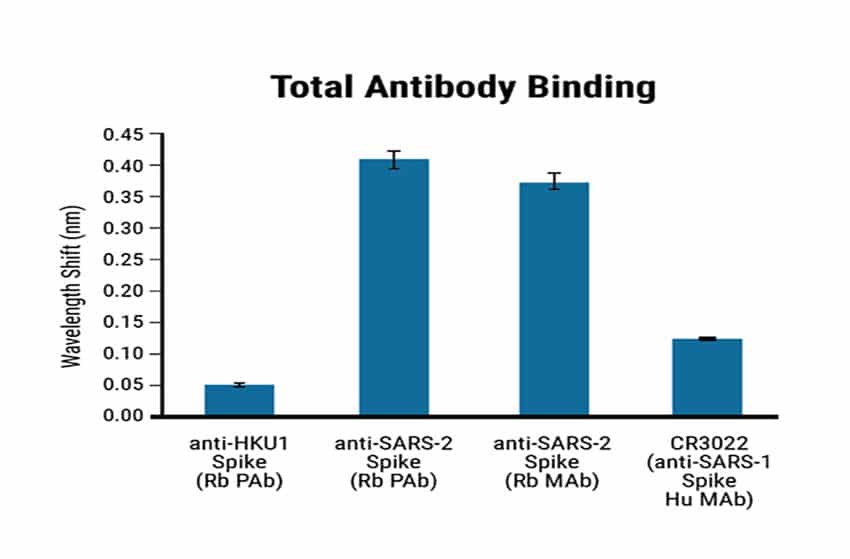

Figure 2. Specificity of the BLI-ISA method using Maxcyte® RDB antigen. BLI-ISA wavelength shift when RBD-biotin-loaded biosensors were dipped into Rabbit polyclonal antibody (Rb PAb), anti-HKU1 Spike (1.5 µg/mL), Rb PAb anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (1.5 µg/mL), rabbit monoclonal antibody (Rb MAb) anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (0.335 µg/mL), or human monoclonal antibody (Hu MAb) anti-SARS-CoV-1 Spike CR3022 (0.2 µg/mL). Error bars represent one standard deviation. Bars represent the mean of biological duplicates. Blue and green dashed lines represent the mean of all seronegative samples plus 3 and 5 standard deviations.
The HCoV-HKU1 antibodies did not cross-react with the SARS-CoV-2 antigen. In contrast, the SARS-CoV-2 antibodies showed a strong signal (Figure 2). The anti-human IgG secondary antibody binds to human antibodies but not to rabbit antibodies. The RBD-biotin antigen produced by MaxCyte® enabled precise identification and quantification of human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2.
Quantitative Assessment of Antibody Levels
Dilution series experiments showed a predictable correlation between sample concentration and signal strength for Total Antibody Binding (Figure 3). BLI-ISA can detect the relative total SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels in moderately and strongly positive samples and qualitatively confirm IgG antibodies at 1:8 dilution. Ambiguous or very weak positive samples could be re-assessed at a higher concentration. Dilution beyond 1:8 may be required for quantitative assessment of IgG levels due to a saturation effect on the biosensor at high concentrations.
Figure 3
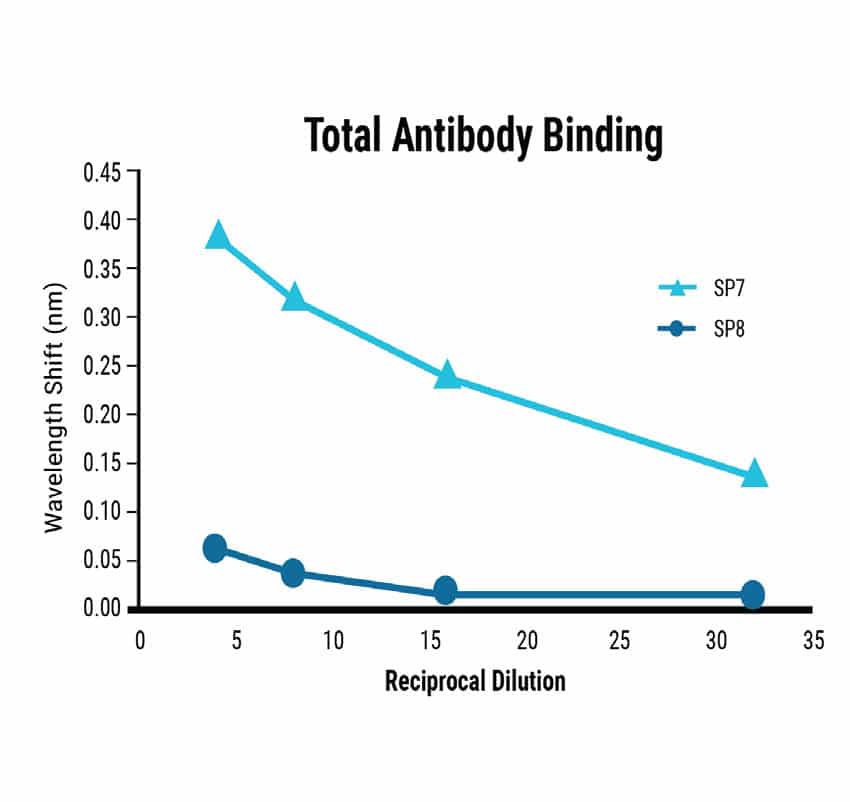
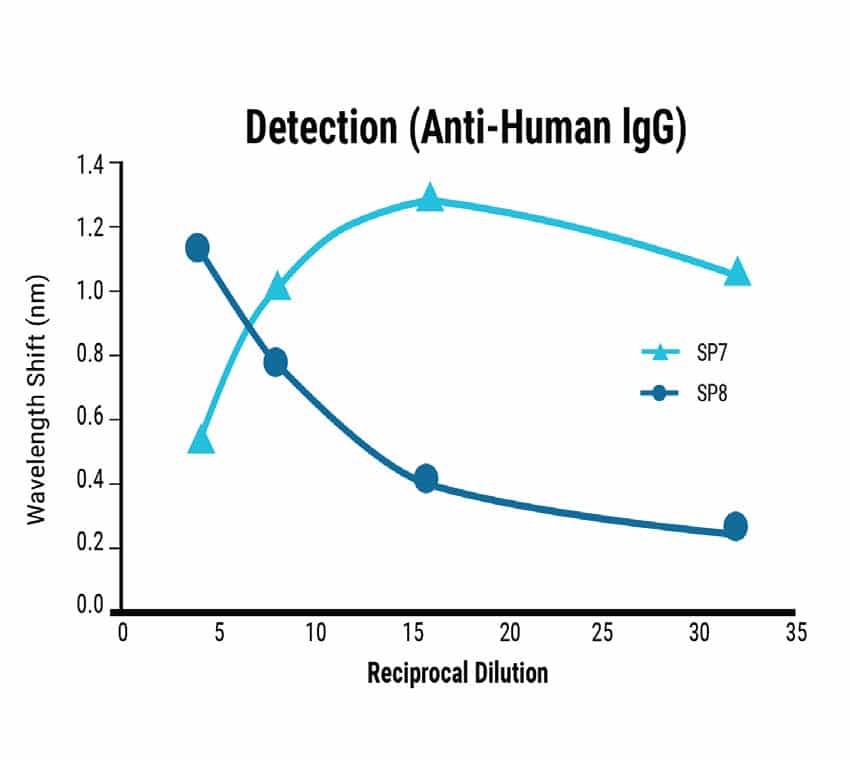
Figure 3. Sensitivity of the BLI-ISA method. Dilution series from strongly (SP7) and moderately (SP8) seropositive samples were tested using the BLI-ISA method to determine assay sensitivity. Detection with anti-human IgG secondary determined the strength of the antibody response in each sample.
Adaptable for Different Antibodies and Antigens
Using a prefusion-stabilized Spike trimer as the antigen showed measurement trends consistent with data from the RBD antigen, although the overall signal was lower. The seropositive (SP) samples showed a negative wavelength shift during the Detection step. The increased size of the prefusion spike compared to RBD changed the sensor’s optical density resulting in these inverted signals.
Adapting the Detection step to quantify IgA rather than IgG worked moderately well. However, the signal was low due to the lower prevalence of IgA in the blood (Figure 4). Overall, these experiments showed that BLI-ISA can be adapted to detect other antigens and antibodies.
Figure 4
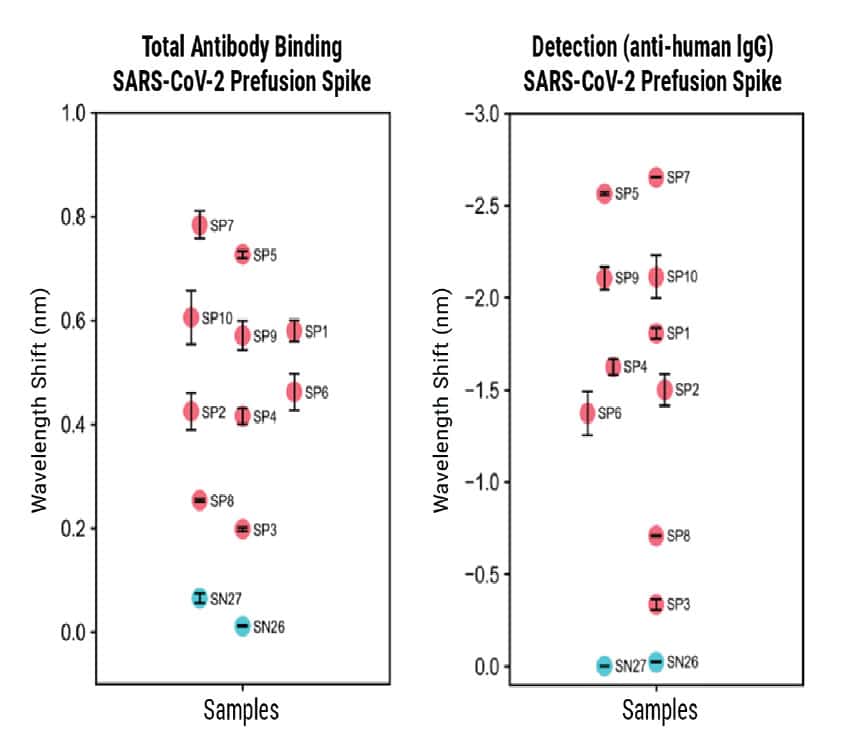
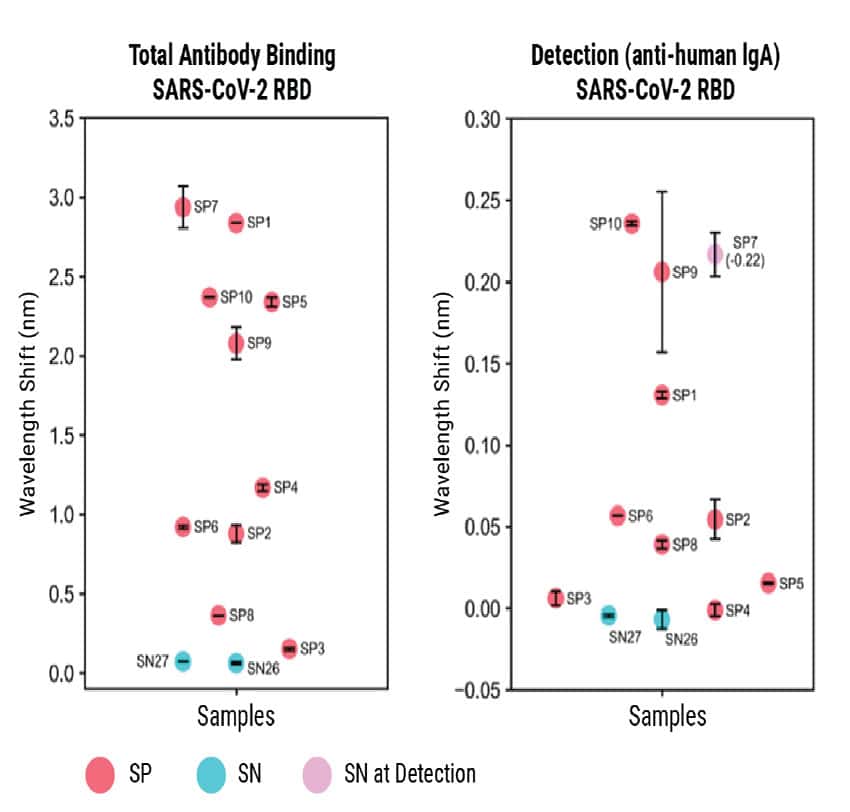
Figure 4. BLI-ISA evaluation of plasma IgG to SARS-CoV-2 prefusion spike and plasma IgA to SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD. BLI-ISA results for selected samples using the SARS-CoV-2 prefusion spike antigen for Total Antibody Binding and IgG Detection (top) or SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD for Total Antibody Binding and IgA Detection (bottom). SN is seronegative, SP is seropositive.
Conclusion and Future Applications
MaxCyte Flow Electroporation® technology enabled the rapid production of large quantities of antigen that were essential for the development of a novel semi-quantitative assay for measuring SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The simple procedure described here is adaptable to the detection of different antigen and antibody isotypes and has the potential to be scaled up for high-throughput screening. The scalability and established regulatory compliance of the MaxCyte ExPERTTM platform is ideally suited to support the advancement of this technology into the clinic. BLI-ISA provides fast and quantifiable antibody data that can be used to study the prevalence and spread of infection, assess the duration of immunity, evaluate interventions and guide vaccine development.
References
- Dzimianski JV, Lorig-Roach N, et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies by biolayer interferometry. Scientific Reports. 2020;10(1). Published 2020 Dec 10 doi:10.1038/s41598-020-78895-x
This content was adapted from Dzimianski et al. 2020 under the Creative Commons license Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)





