Scientific brief
Off-Target Effects of CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing in Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells
Paving the Way for Accelerated Clinical Development of Adoptive Cell Therapies
Precision genome engineering requires technologies that allow efficient and reproducible delivery of DNA, mRNA and Ribonucleoprotein (RNP)-based reagents into a range of primary and stem cells. In addition, clinical gene editing requires a transfection platform that is inert and does not affect genome stability and cell viability. The CRISPR-Cas9 system of genome editing has the potential to treat a variety of genetic diseases. However, unintended off-target double-stranded breaks introduced by Cas9 cleavage could have unforeseen clinical complications. Here we share data characterizing genome integrity in clinically relevant human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) following transfection of CRISPR-Cas9 using MaxCyte®. There was no evidence of significant structural or nucleotide sequence variations within the genomes of clonal isolates from human HSPCs following electroporation and/or Cas9 treatment.
Experimental Design
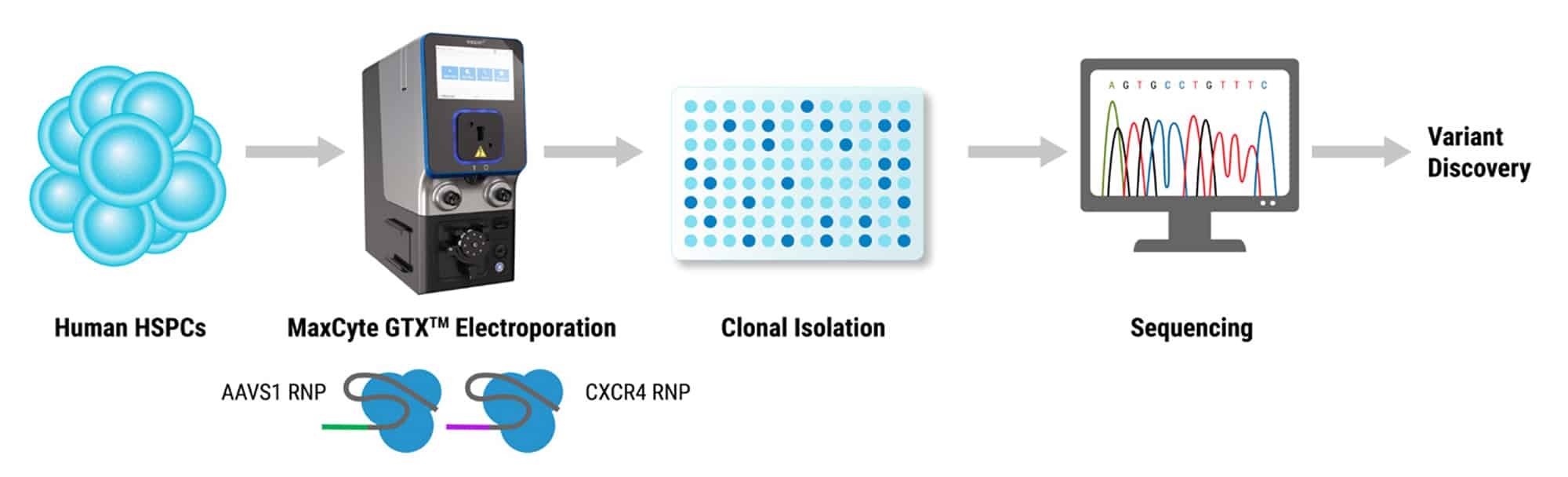
Primary human HSPCs were electroporated using two Cas9 RNPs that were engineered to target two separate loci, CXCR4 and AAVS1. Gene-edited HSPCs and controls were then subject to single cell cloning in 96 well plates. Whole genome sequencing (WGS) and bioinformatic analysis were performed as an unbiased method of assessing genomic integrity and characterization of Cas9 activity.
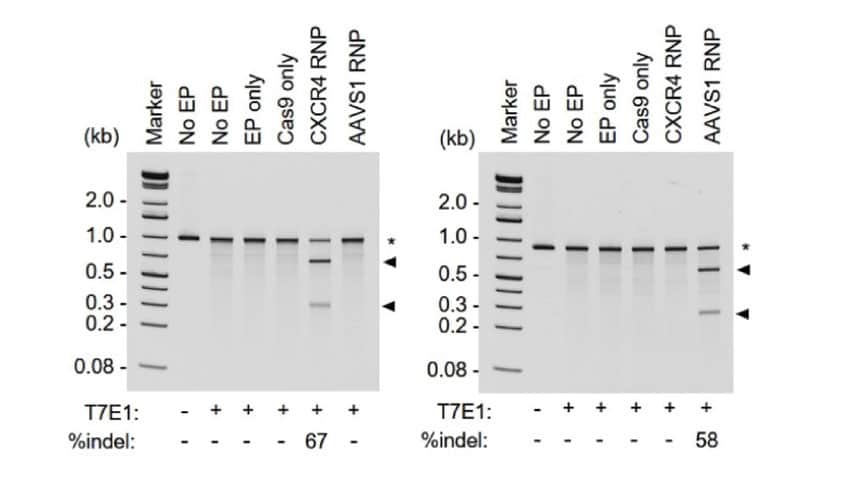
A. High efficiency on-target editing in bulk HSPC populations
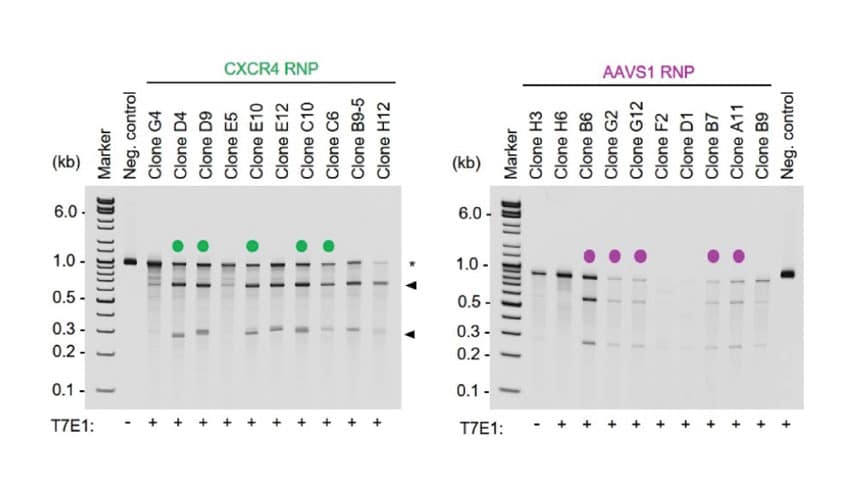
B. Successful gene editing in clonal isolates
C. Characterization of off-target InDels
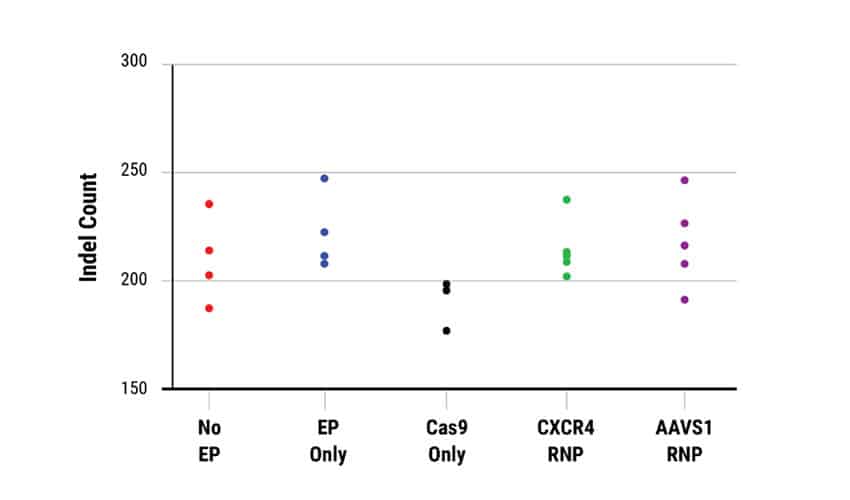
D. Characterization of off-target single nucleotide variants
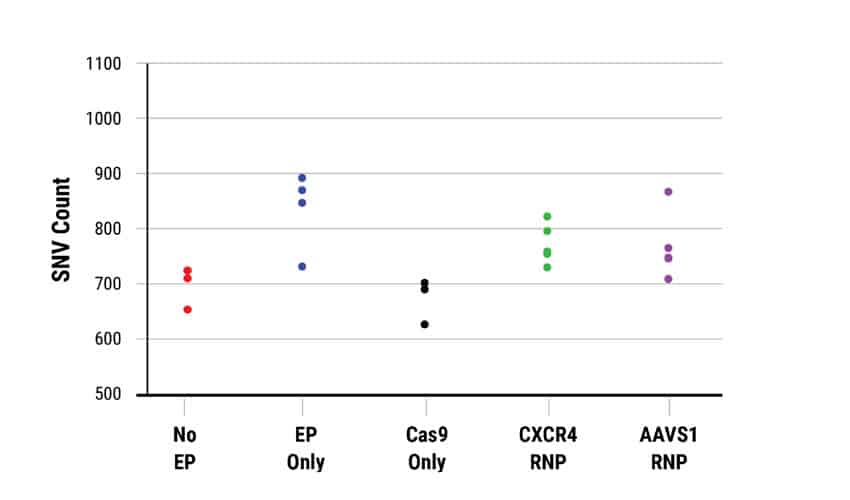
Genome-wide sequencing analysis of CRISPR-Cas9 activity in human HSPCs.
Editing efficiency was determined in A) bulk (pre-clonal) HSPC and B) cellular clones using a T7E1 assay. On-target InDel formation in bulk HSPCs was 67% for CXCR4 (left) and 58% AAVS1 (right). Gene editing efficiencies were high, given the accepted limits of sensitivity of the T7E1 assay. Clonal isolates selected for WGS analysis are indicated by a color-coded dot. No EP=non-electroporated cells; EP Only=Cells electroporated without CRISPR RNP; Cas9 Only=Cells electroporated without gRNA. WGS revealed a total of C) 4474 off-target InDels and D) 15,855 off-target single nucleotide variants (SNVs) distributed among all the samples. The majority of InDels and SNVs appeared within intergenic or non-protein coding regions within the genome. Electroporated cells and untreated cells displayed similar distributions of both InDels and SNVs regardless of the presence of Cas9 RNPs.
Summary
- The high efficiency and low toxicity of MaxCyte® electroporation ensures highly targeted gene disruption frequencies with negligible off-target effects that bolster therapeutic efficacy.
- Gene editing using MaxCyte non-viral engineering enables rapid development of next-generation adoptive cell therapies for treatment of a wide variety of diseases.
- MaxCyte electroporation technology efficiently delivers a diversity of payloads including mRNA, sgRNA, and RNPs to difficult-to-engineer primary cells commonly used for adoptive cell therapies including hematopoietic stem cells and T cells.
- MaxCyte electroporation enables high levels of gene editing including:
- Gene knockout/disruption
- Gene knockin
- Single nucleotide gene mutation correction
- Development and optimization of MaxCyte electroporation for new cell types and payloads is a rapid, straightforward process.
References
- Smith R, Chen Y, Seifuddin F, et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Off-Target CRISPR-Cas9 Activity in Single-Cell-Derived Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell Clones. Genes. 2020;11(12):1501. Published 2020 Mar 13. doi :10.3390/genes1121501





